Everything You Need To Know About Ethernet Network Communication
 In terms of computing and networking, the Ethernet or the Local Area Network (LAN), MAN and WAN of computer systems that we use for commercial purposes or otherwise has a rich set of protocols and formatting regulations that enable a smooth network connection. It is responsible for the clear and smooth transmission of data across network devices as well as over the network connection.
In terms of computing and networking, the Ethernet or the Local Area Network (LAN), MAN and WAN of computer systems that we use for commercial purposes or otherwise has a rich set of protocols and formatting regulations that enable a smooth network connection. It is responsible for the clear and smooth transmission of data across network devices as well as over the network connection.
In order for the Ethernet to control, monitor and regulate data being transmitted across networks, it makes use of specific technology and features including an Ethernet gateway. Let’s learn more about how the Ethernet facilitates communication across networks.
What is an Ethernet gateway?
An Ethernet gateway, sometimes called a router is basically a node or one of the communication endpoints in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol Suite that is responsible for forwarding data packets to other networks in cases where the network protocols are similar.
In other words, a default gateway serves as a router or a forwarding host to redirect data packets, while also being a common access point to other networks. This may involve not just address changes but also completely different networking technologies with different network prefixes as well. Such gateways are called internet gateways.
Now both the internet gateway and the router or the Ethernet gateway, are nodes that connect and regulate traffic between two or more networks. But the type of networks being handled is what is different.
A Windows 2000 network that uses the TCP/IP internet protocol as its primary protocol can use a router or an Ethernet gateway to connect to the internet as it is the same primary protocol that the internet uses.
An internet gateway on the other hand would be used to connect a Windows NT network for example with a NetWare network.
How does the Ethernet gateway work?
The Ethernet gateway is always connected to two or more different data lines from different networks. It reads the destination IP addresses on data packets coming in from the data lines and determines the ultimate destination. Then it makes use of the information on its routing table or the Routing Information Base (RIB) and directs the data packet to the next network on its route or journey. RIB is basically a data table that has a list of routes to particular destination addresses and sometime even the distance information associated with these routes.
The Ethernet also makes use of Ethernet converters and serial to Ethernet converters for converting media and data signals.
What is an Ethernet converter?
An Ethernet converter also called an Ethernet media converter is basically a device that is designed to enable the communication and smooth connection between different networking media such as fibre and co-axial cables used by different networks. It usually comes in the form of a small box and typically it is used to connect fibre media coming from an optical fibre based network and a copper-based network which is more conventional.
What is a serial to Ethernet converter?
Just like the media used by different networks, the data signals across networks may also come in serial form, which need to be converted to Ethernet packets in order to be routed and processed. This job is done by serial to Ethernet converters which are also called terminal servers or device servers as they are devices that have their own IP address.
It basically is a device that converts serial RS232, RS485 or RS422 data to Ethernet packets and also Ethernet TCP/IP packets back to these serial data signals. It comes in different models that facilitate different conversions.
How does a serial to Ethernet converter work?
A serial to Ethernet converter device usually comes with driver software that you need to install on your PC. The program creates virtual COM ports within the system when the converter is connected to the system. You can see all the virtual ports created by the software on your device manager list.
When you connect a serial device to one of the hardware ports on your converter device, the peripheral gets redirected to the visual serial port of your system and is identified by your PC as a local device. The circuitry within the converter then goes about converting each of the signals to Ethernet data packets for effective communication.




 FactoryTalk services platform is a suite of services developed by Rockwell Software. It includes Alarm and Events, Activation, Security, Audit, Directory, and Live Data. FactoryTalk is not a product that can be purchased as a standalone software package. FactoryTalk is embedded in most of the products from Rockwell Software; that is, it is the prefix to the majority of the Rockwell Software’s products.
FactoryTalk services platform is a suite of services developed by Rockwell Software. It includes Alarm and Events, Activation, Security, Audit, Directory, and Live Data. FactoryTalk is not a product that can be purchased as a standalone software package. FactoryTalk is embedded in most of the products from Rockwell Software; that is, it is the prefix to the majority of the Rockwell Software’s products. FactoryTalk Viewpoint is an extension to the PanelView Plus and the View Site Edition, which adds web server features to the FactoryTalk View project.
FactoryTalk Viewpoint is an extension to the PanelView Plus and the View Site Edition, which adds web server features to the FactoryTalk View project.  Simply put, Modbus is basically a protocol that facilitates communication between the “master” or the host and the “slaves” or the connected devices. It enables the host to read the measures and aids in the configuration of devices.
Simply put, Modbus is basically a protocol that facilitates communication between the “master” or the host and the “slaves” or the connected devices. It enables the host to read the measures and aids in the configuration of devices.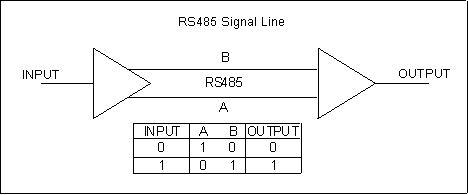 Hence, when we say Modbus RS485, it denotes the protocol being used in process automation along with its ability to communicate effectively by the name of serial transmission standard.
Hence, when we say Modbus RS485, it denotes the protocol being used in process automation along with its ability to communicate effectively by the name of serial transmission standard.