The Difference Between Profibus And Profinet
Profibus and Profinet are two terms that are often confused with each other, both of them being field networks part of industrial automation protocols. However, there are significant differences between the two in various aspects and for the same reason are used for different purposes in industries.
In order to clearly understand their functioning and application of the two, it is important to first get a good grasp of the basics.
The basics
Profibus which is the acronym for Process Field Bus is basically a standard for fieldbus communication used in automation technology. Profinet on the other hand, which is acronym for Process Field Net is a standard for internet communication over industrial Ethernet.
As they are both very popular and highly sought after automation protocols created by the same organization, they do share a number of similarities. They are both created and maintained by Profibus and Profinet International.
However, Profinet comparatively has extra advanced capabilities that facilitate a faster and a more flexible field of communication within a network.
 They share the same application profiles; which essentially implies that they have similar guidelines followed by different categories of devices within a network, regarding their use of Profibus and Profinet data during communication. These profiles enable smooth planning and functioning of the automation systems and devices.
They share the same application profiles; which essentially implies that they have similar guidelines followed by different categories of devices within a network, regarding their use of Profibus and Profinet data during communication. These profiles enable smooth planning and functioning of the automation systems and devices.
Other than that they are also very similar in terms of their engineering concepts and they use General Station Description files to define the hardware for each device. The file type however is different.
In simple terms Profibus is a classic and traditional automation protocol based on serial communication while Profinet is a newer enhanced automation protocol based on Industrial Ethernet.
Significant points of differences
Profibus and Profinet use GSD files for define the hardware for various devices. But as mentioned before, the difference lies in the type of file being used. Profibus uses ASCII files whereas Profinet uses XML files.
In terms of their base field, Profinet made the move from RS-485 to Ethernet to become more efficient and ubiquitous. It is a more adaptable and modern technology that helps organizations future-proof their processes.
Besides that, being based on industrial Ethernet, Profinet also enjoys a higher bandwidth, a larger size of message and unlimited amounts of address space. Separate controllers attached to the network may have to adhere to certain limitations in terms of address space, depending on their memory capacity and processor capabilities though.

Other than that, Profinet is faster than Profibus because of the provider/consumer model that it uses, where any node in the network is allowed to communicate at any given time. Hence, there is no delay in information exchange.
Besides that, Ethernet networks are generally switched networks that are practically devoid of network collisions.
Profibus uses a master/slave approach rather than a provider/ consumer model where the master is usually in charge of the entire network and the nodes are allowed to communicate only when prompted.
Usually industrial enterprises are required to deploy separate gateways in order to communicate with other networks. However, with Profinet, it creates its own proxies for translation and data exchange between two different networks and unlike an ordinary gateway they are defined in an open standard.
In case of Profibus, there is a facility for wireless transmission of messages; however, it requires similar based proprietary radios at both ends.
As Profinet works on standard Ethernet, it can easily use WiFi or Bluetooth for wireless transmission.
Even though Profinet is an enhanced and more versatile version of Profibus, it does not mean that the former can be used across industries regardless of the processes. It is important to study the field of automation and choose the protocol accordingly.
Image sources:
https://w3.usa.siemens.com/automation/us/en/industrial-controls/products/industrial-communications/profinet/pages/profibus-to-profinet.aspx
https://www.rtaautomation.com/technologies/profinet-io/


 Communication software has come a long way from basic emails and chat systems now. Advanced technologies these days provide more than just a mechanism for different systems and users to exchange files and terminal emulators among themselves.
Communication software has come a long way from basic emails and chat systems now. Advanced technologies these days provide more than just a mechanism for different systems and users to exchange files and terminal emulators among themselves. In terms of computing and networking, the Ethernet or the Local Area Network (LAN), MAN and WAN of computer systems that we use for commercial purposes or otherwise has a rich set of protocols and formatting regulations that enable a smooth network connection. It is responsible for the clear and smooth transmission of data across network devices as well as over the network connection.
In terms of computing and networking, the Ethernet or the Local Area Network (LAN), MAN and WAN of computer systems that we use for commercial purposes or otherwise has a rich set of protocols and formatting regulations that enable a smooth network connection. It is responsible for the clear and smooth transmission of data across network devices as well as over the network connection.


 FactoryTalk services platform is a suite of services developed by Rockwell Software. It includes Alarm and Events, Activation, Security, Audit, Directory, and Live Data. FactoryTalk is not a product that can be purchased as a standalone software package. FactoryTalk is embedded in most of the products from Rockwell Software; that is, it is the prefix to the majority of the Rockwell Software’s products.
FactoryTalk services platform is a suite of services developed by Rockwell Software. It includes Alarm and Events, Activation, Security, Audit, Directory, and Live Data. FactoryTalk is not a product that can be purchased as a standalone software package. FactoryTalk is embedded in most of the products from Rockwell Software; that is, it is the prefix to the majority of the Rockwell Software’s products. FactoryTalk Viewpoint is an extension to the PanelView Plus and the View Site Edition, which adds web server features to the FactoryTalk View project.
FactoryTalk Viewpoint is an extension to the PanelView Plus and the View Site Edition, which adds web server features to the FactoryTalk View project.  Simply put, Modbus is basically a protocol that facilitates communication between the “master” or the host and the “slaves” or the connected devices. It enables the host to read the measures and aids in the configuration of devices.
Simply put, Modbus is basically a protocol that facilitates communication between the “master” or the host and the “slaves” or the connected devices. It enables the host to read the measures and aids in the configuration of devices.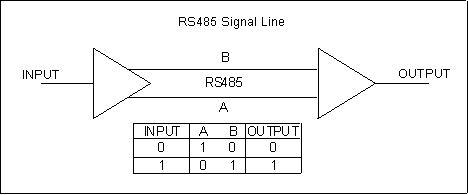 Hence, when we say Modbus RS485, it denotes the protocol being used in process automation along with its ability to communicate effectively by the name of serial transmission standard.
Hence, when we say Modbus RS485, it denotes the protocol being used in process automation along with its ability to communicate effectively by the name of serial transmission standard. What is Allen Bradley?
What is Allen Bradley?